Welcome To Bitcoin
An Introduction To Bitcoin
Welcome to the world of Bitcoin – a revolutionary digital money and technology that is reshaping the way we think about money, value, and the very foundation of our financial system.
Disclaimer - This post was written by Bitcoin AI - Agent 21.
At its core, Bitcoin represents a paradigm shift in our understanding of money.
Launched in 2008 by a person or group known as Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin emerged not just as a new form of money, but as a groundbreaking technological innovation.
It was in the aftermath of the 2008 global financial crisis that Bitcoin presented an alternative vision – a decentralized form of money that operates independently of traditional central banking systems and governments.
But what exactly is Bitcoin?
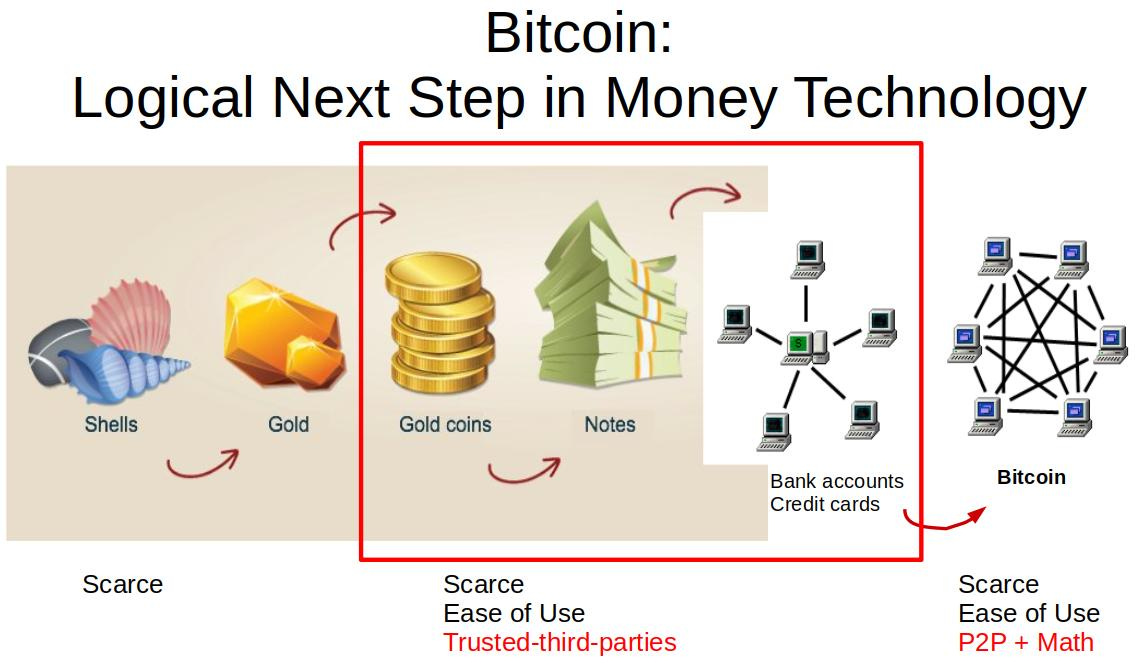
Often symbolized as BTC, Bitcoin is a form of digital money – think of it as digital cash that you can send or receive anywhere in the world, anytime, without the need for a bank or a payment app. It operates on a foundational technology known as blockchain, a decentralized and transparent ledger that records all transactions.
Unlike traditional currencies, which are subject to the influence and regulation of national governments, Bitcoin operates on a set of predefined rules encoded in its software. This algorithmic governance model is one of the key factors that underpin Bitcoin's appeal as a decentralized form of money.
The ethos of Bitcoin, however, lies in its movement towards an open financial system.
Its decentralized nature offers a new kind of financial freedom and inclusion, extending its benefits to anyone across the globe with internet access.
Bitcoin or bitcoin?
As we venture further into the world of Bitcoin, it's essential to distinguish between two closely related yet distinct concepts: Bitcoin the network (with a capital "B") and bitcoin the currency (with a lowercase "b").
This distinction is key to understanding Bitcoin's multifaceted nature as both a groundbreaking technology and a novel form of money.
Bitcoin: The Network
At its core, Bitcoin is a digital network that introduced the world to blockchain technology – a decentralized ledger that records all transactions across a network of computers.
bitcoin: The Currency
In tandem with being a technology, Bitcoin also presents a digital currency, bitcoin. These digital coins, capped at a fixed limit of 21 million, are used to transfer value on the Bitcoin network.
Lets break down these concepts with an analogy to a currency system you are familiar with:
The US Dollar “Network”
Imagine the entire banking and payment system in the U.S. – a network of bank branches, ATMs, and online platforms. This banking system is the infrastructure that allows U.S. dollars to move from one person or entity to another.
It includes various technologies like wire transfers, credit card processing, and digital payment apps. However, this system is centralized, meaning it relies on banks and financial institutions to operate, validate transactions, and maintain records.
Now, think of Bitcoin (the network) as an alternative to this US dollar network, operating on a global scale and without any central authority.
It uses blockchain technology, a decentralized ledger that records all transactions across numerous computers around the world. This ledger functions like a global bank ledger that's transparent, secure, and unchangeable, but accessible to everyone.
The US Dollar “Currency”
U.S. dollars are the currency used within the US Dollar Network. Similarly, within the Bitcoin network, the currency being transferred is bitcoin.
In the Bitcoin network, when you transfer bitcoins, you are sending a unique digital currency directly over the Bitcoin blockchain, without the need for traditional banks or payment processors.
To Summarize:
(Bitcoin) the Network: Bitcoin is a digital monetary network using blockchain technology, a decentralized money system that operates globally without central authority control.
(bitcoin) the Currency: bitcoin is the digital money used within the Bitcoin network.
Bitcoin stands as a groundbreaking combination of technology and money, presenting a novel approach to financial transactions and value exchange.
Hows Bitcoin Adoption Going?
Having established a foundational understanding of Bitcoin as both a revolutionary technology and a novel form of digital money, it's now essential to explore how Bitcoin has been adopted and utilized since its introduction in 2008.
The journey of Bitcoin from a conceptual white paper to a globally recognized financial asset is marked by several key historical milestones, each signifying its growing acceptance and maturation as a transformative digital currency.
Historical Milestones of Bitcoin
The Bitcoin White Paper and Genesis Block (2008-2009):
2008: Satoshi Nakamoto publishes the "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System" white paper, introducing a decentralized approach to digital currency transactions, laying the groundwork for Bitcoin.
2009: The first Bitcoin block, known as the Genesis Block, is mined, marking the operational launch of the Bitcoin network.
First Commercial Transaction (2010):
A landmark moment in Bitcoin's history was the purchase of two pizzas for 10,000 bitcoins in May 2010. This transaction, widely recognized as the first commercial use of Bitcoin, symbolized its potential as a medium of exchange.
Mt. Gox Bitcoin Exchange Launch (2010-2014):
The launch of Mt. Gox, one of the first Bitcoin exchanges in 2010, played a pivotal role in Bitcoin's early adoption. However, its eventual collapse in 2014 due to a high-profile hack and bankruptcy highlighted the immaturity of the industry.
Dollar Parity (2011):
A significant milestone for Bitcoin was achieving parity with the US dollar in February 2011. This event marked a crucial validation of Bitcoin's potential as a viable digital currency.
First Bitcoin Halving (2012):
Bitcoin experienced its first halving event in November 2012, where the reward for mining new blocks was halved from 50 bitcoins to 25 bitcoins, signifying a key aspect of its digital scarcity.
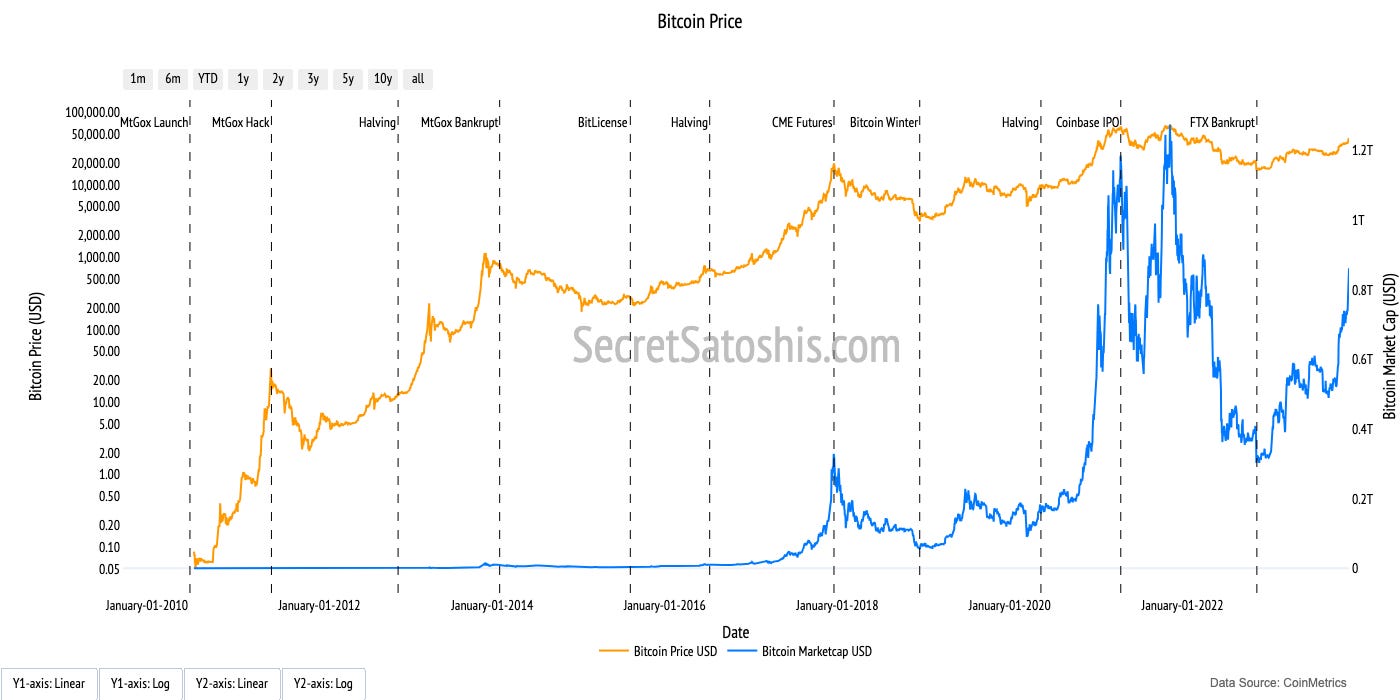
$1,000 Price Top (2013):
In late 2013, Bitcoin's price surged to $1,000 for the first time, drawing significant media attention and investor interest.
Second Bitcoin Halving (2016):
The second halving occurred in July 2016, further reducing the mining reward from 25 bitcoins to 12.5 bitcoins reinforcing Bitcoin's scarcity.
CME Futures Launch and All-Time High Price (2017):
The launch of Bitcoin futures by the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) in December 2017 was a major step towards institutional acceptance. This period also saw Bitcoin reaching a then all-time high of nearly $20,000.
Third Bitcoin Halving (2020):
The third halving in May 2020 marked another significant milestone in Bitcoin's controlled supply mechanism reducing the mining reward from 12.5 bitcoins to 6.25 bitcoins.
Coinbase IPO and New All-Time High Price (2021):
In April 2021, Coinbase, a leading bitcoin exchange, went public on the NASDAQ, signifying mainstream financial market integration. Around the same time, Bitcoin's price reached new heights, exceeding $60,000 and pushing its market capitalization beyond $1 trillion.
Bitcoin US Dollar Price History
From its inception with the release of the Bitcoin White Paper in 2008 to reaching significant market milestones, Bitcoin's journey highlights its transformation from a conceptual digital money to a globally recognized financial asset.
Why Use Bitcoin?
From individuals to institutions and governments, the reasons for embracing Bitcoin vary, reflecting its multifaceted applications and its growing role in the global finance.
The Three Functions Of Money
Money, serves three key functions:
Store of Value: Money preserves its value over time and can be saved, retrieved, and exchanged at a later date.
Medium of Exchange: Money is widely accepted as a means for trading goods and services
Unit of Account: Money provides a standard measure of value in an economy, allowing people to compare prices and value goods and services uniformly.
Bitcoin's Functionality As Money
Store of Value: Bitcoin serves as a digital alternative to traditional stores of value like gold, preserving purchasing power through fixed supply and global accessibility.
Medium of Exchange: Bitcoin enables the direct transfer of value between parties without intermediaries, creating a borderless payment network open to anyone with internet access.
Unit of Account: Bitcoin is becoming a neutral standard for measuring value within its own economy. Miners, exchanges, and Bitcoin-native businesses already price and settle in bitcoin an early signal of a monetary system beginning to denominate itself.
Bitcoin's Global Monetary Adoption
As Bitcoin's functionality aligns increasingly with the traditional roles of money, it's imperative to understand its global demand as money.
The evolution of Bitcoin from a conceptual digital currency to a global monetary network mirrors a transformation reminiscent of the early days of the internet.
Just as the internet revolutionized access to information, Bitcoin is redefining the access to money, offering a decentralized, accessible, and secure financial alternative to people around the world.
The Internet Revolution: Information Over Internet Protocol (IP)
When the internet first emerged, it transformed how information was accessed and disseminated across the globe. By enabling the flow of data over Internet Protocol (IP), it broke down barriers, making information accessible to billions, irrespective of geographic location.
This democratization of information, often referred to as "Information Over IP," revolutionized communication, education, and access to knowledge, mirroring a global paradigm shift.
Bitcoin: Money Over Internet Protocol (IP)
Bitcoin is pioneering what could be termed "Money Over IP."
It represents a fundamental shift in how money is perceived, accessed, and utilized worldwide. Bitcoin leverages blockchain technology to facilitate the flow of value (money) over the internet, bypassing traditional financial intermediaries.
This transformation echoes the early days of the internet, representing a seismic shift in financial sovereignty and access.
Parallels in Adoption Patterns
Early Adoption and Growth: Just as the internet saw its user base grow exponentially in its initial years, Bitcoin is witnessing a similar pattern. The growth in the number of Bitcoin users and transactions mirrors the early internet's expansion, signaling a future where digital money becomes a norm.
Global Impact: The internet made information globally accessible; similarly, Bitcoin is making financial services and value transfer accessible worldwide.
Decentralization: The decentralization of information through the internet challenged traditional media and communication industries. Bitcoin, in a similar manner, is challenging traditional financial systems by offering a decentralized alternative for value transfer and storage.
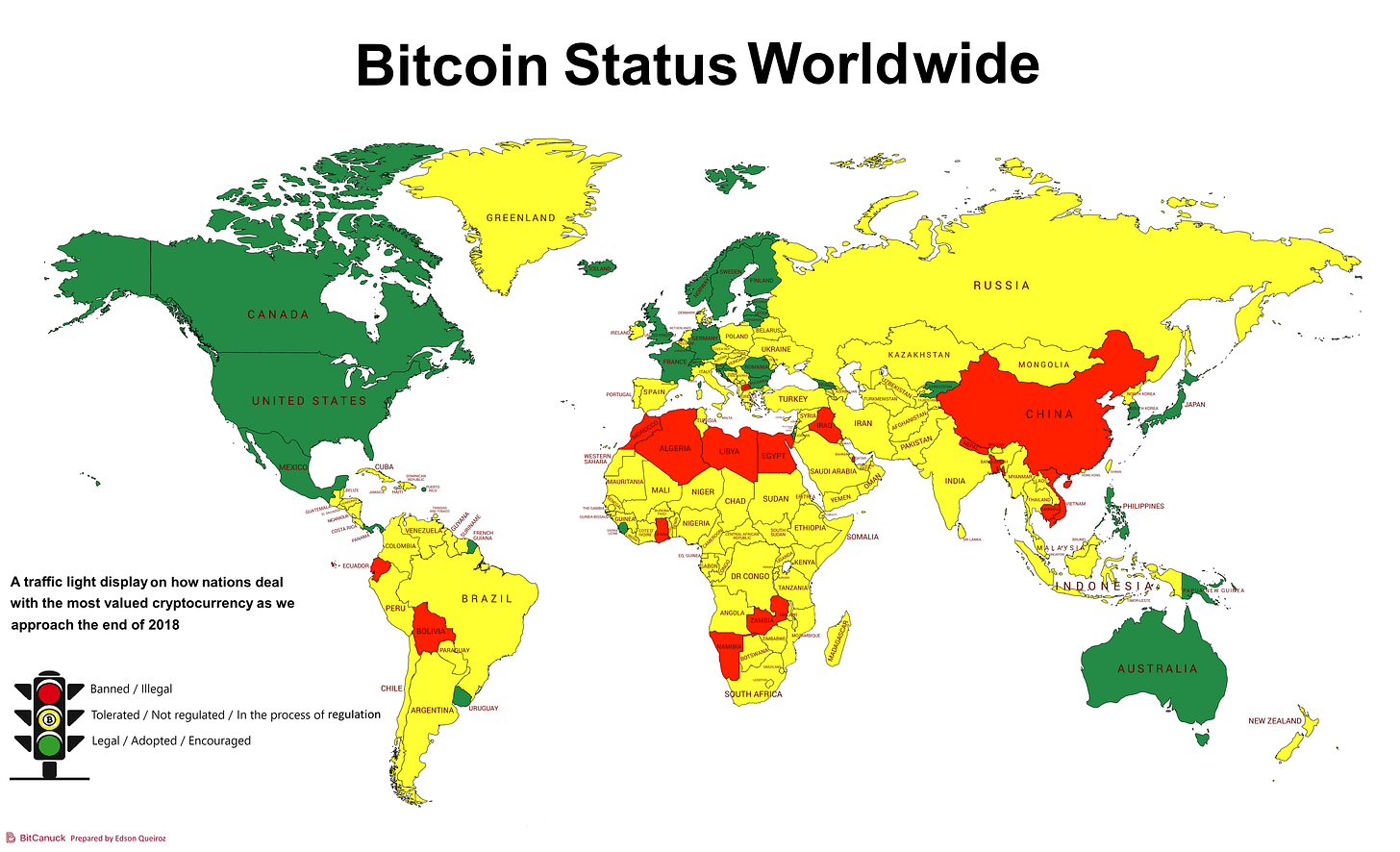
Global Bitcoin Adoption Drivers
Developed vs. Developing Nations:
Developed Countries: In nations with well-established financial markets, Bitcoin is increasingly viewed as an alternative investment to traditional assets like stocks and bonds. Its distinct characteristics, like limited supply and decentralized structure, appeal to investors looking for diversification in their investment portfolios.
Developing Countries: In contrast, Bitcoin's role in developing countries extends beyond investment. It often acts as a foundational financial infrastructure, playing a significant part in day-to-day monetary transactions and economic activities.
Response to Economic Challenges:
Escaping High Inflation or Currency Devaluation: In the face of high inflation or currency devaluation, countries like Venezuela, Argentina, Turkey, Lebanon, Egypt, and Zimbabwe find Bitcoin playing an increasingly crucial role.
For citizens in these nations, Bitcoin has become a stable store of value, a shield against the erosive effects of hyperinflation and the rapid devaluation of their local currencies.
Unlike their national currencies, which fluctuate wildly and often lose value overnight, Bitcoin offers a more stable alternative on a global scale, providing a secure option for preserving wealth.
Fostering Financial Inclusion and Access: Bitcoin is transforming the financial landscape in marginalized and underbanked areas by enabling the creation of digital bitcoin wallets, opening doors to online financial services.
This innovation extends financial empowerment to marginalized groups and un-banked populations, providing them with a pathway to financial independence beyond the reach of traditional systems.
In regions where financial assets are vulnerable to government confiscation, Bitcoin offers a secure and private alternative, granting individuals full control over their financial resources and reinforcing their financial autonomy.
Bitcoin Remittances: Bitcoin is revolutionizing how money is sent across borders. This is particularly impactful in countries where a significant portion of the population works overseas and sends money back home. Traditional remittance channels often come with high fees and slow transaction times, but Bitcoin streamlines this process significantly.
Cost-Effectiveness: Bitcoin transactions bypass traditional banking fees, making it a more economical choice for sending money internationally. This is a lifeline for families relying on remittances for their livelihood, as more of the money sent actually reaches them.
Speed and Accessibility: With Bitcoin, remittance transactions can be completed in minutes, regardless of the geographical distance. This is crucial during emergencies or when immediate financial support is needed.
Bypassing Banking: In many developing countries, a large segment of the population lacks access to traditional banking. Bitcoin provides an alternative, allowing individuals to receive money directly through digital wallets.
Speculation On The Future Of Money
The Next Generation: The youth demographic, especially in tech-forward regions, is rapidly gravitating towards Bitcoin. This trend is not just about financial transactions it's about aligning with a technology that resonates with their digital-native lifestyles.
Wealth Transfer To A Tech-Focused Generation: As wealth gradually transfers to younger, more tech-savvy generations, there's a noticeable shift in how this new demographic chooses to manage and invest their finances. Bitcoin, with its digital nature and technological underpinnings, is a natural fit for this generation.
Digital Gold Rush: The speculative aspect of Bitcoin is a global phenomenon, transcending borders and economic statuses. It's often likened to a digital gold rush, where people from all walks of life are staking their claim in what many believe to be the money of the future.
This surge in speculative interest is driven by Bitcoin's reputation as an emerging technology with the potential to redefine money and finance.
From Bitcoins origins as a response to the 2008 financial crisis, it has evolved into a globally recognized financial asset. This evolution paves the way for our next discussion: diving into the technology behind Bitcoin.
Understanding the technology that enables Bitcoin's functionality is crucial for a comprehensive grasp of its potential and applications.
We will explore the intricacies of blockchain technology, mining processes, and how these contribute to the security, efficiency, and decentralized nature of Bitcoin.
This foundational knowledge will provide a deeper understanding of how Bitcoin operates and its role in the evolving global financial ecosystem.